|
Relationships and Keys
A relationship is an association between two or more tables. Relationships are expressed in the data values of the primary and foreign keys.
A primary key is a column or columns in a table whose values uniquely identify each row in a table. A foreign key is a column or columns whose values are the same as the primary key of another table. You can think of a foreign key as a copy of primary key from another relational table. The relationship is made between two relational tables by matching the values of the foreign key in one table with the values of the primary key in another.
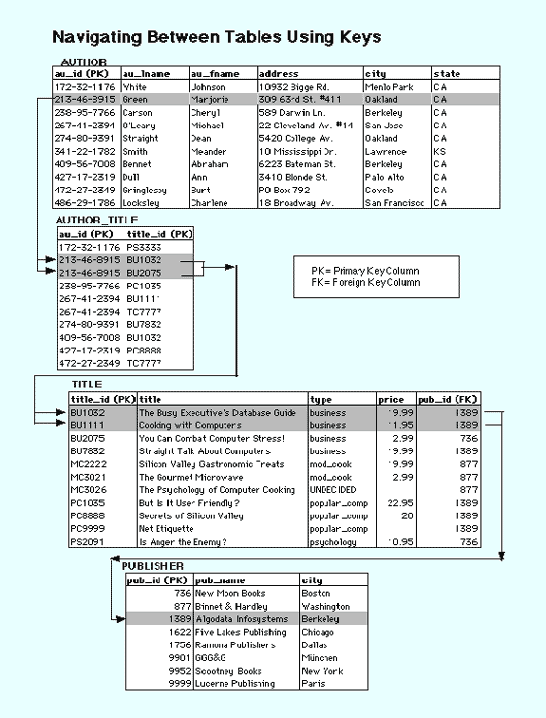
Keys are fundamental to the concept of relational databases because they enable tables in the database to be related with each other. Navigation around a relational database depends on the ability of the primary key to unambiguously identify specific rows of a table. Navigating between tables requires that the foreign key is able to correctly and consistently reference the values of the primary keys of a related table. For example, the figure below shows how the keys in the relational tables are used to navigate from AUTHOR to TITLE to PUBLISHER. AUTHOR_TITLE is an all key table used to link AUTHOR and TITLE. This relational table is required because AUTHOR and TITLE have a many-to-many relationship.
Data Integrity
Data integrity means, in part, that you can correctly and consistently navigate and manipulate the tables in the database. There are two basic rules to ensure data integrity; entity integrity and referential integrity.
The entity integrity rule states that the value of the primary key, can never be a null value (a null value is one that has no value and is not the same as a blank). Because a primary key is used to identify a unique row in a relational table, its value must always be specified and should never be unknown. The integrity rule requires that inset, update, and delete operations maintain the uniqueness and existence of all primary keys.
The referential integrity rule states that if a relational table has a foreign key, then every value of the foreign key must either be null or match the values in the relational table in which that foreign key is a primary key.
|
